This website serves the purpose of providing general information and does not in any way replace medical or specialist advice. Consult a healthcare practitioner if symptoms worsen or persist.
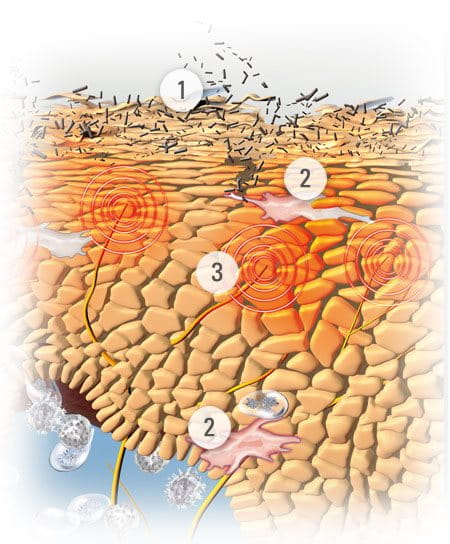
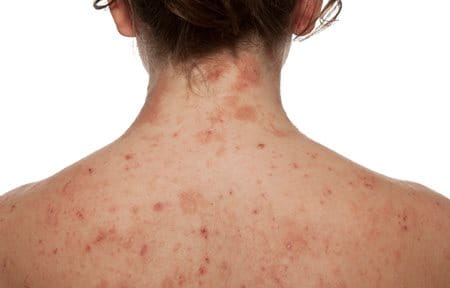
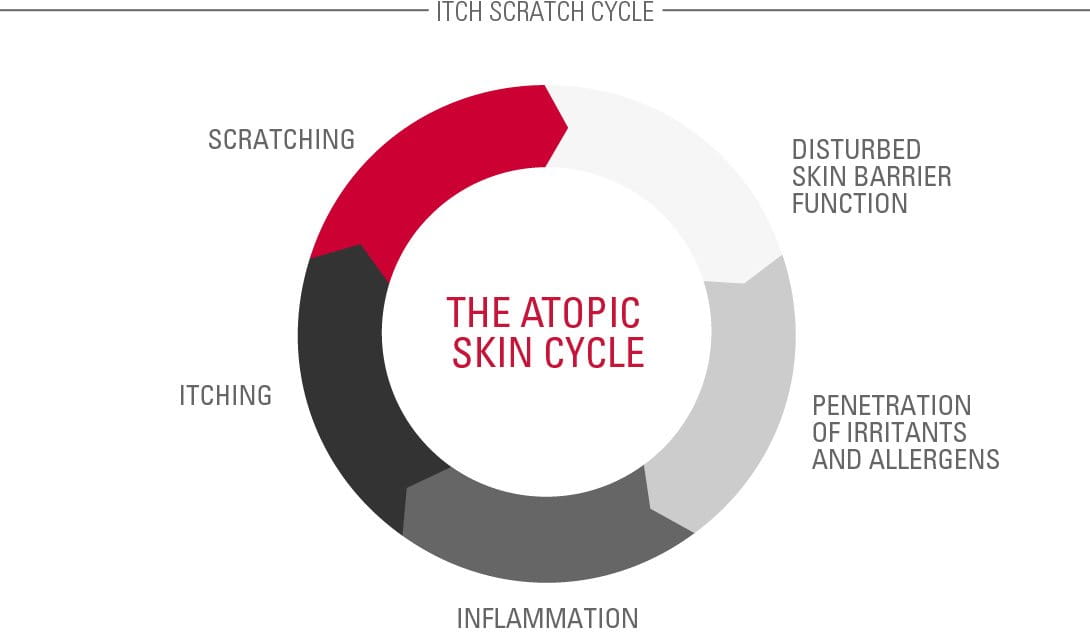
Atopic Dermatitis is a skin disease that affects between 2-5% of adults and as many as 10-20% of children globally. It is a chronic, long-term condition characterised by dry, flaky, irritable skin and occasional flare-ups with more distressing symptoms. While there’s no known cure, regular and consistent skin care can protect skin.
Try Eucerin’s Eczema Relief range with Colloidal Oatmeal and Ceramide 3 for Eczema-prone skin.